Drones are more than just an innovative way to patrol and review electric delivery lines. They can be an innovative tool to help string them, too.
At least twice in recent weeks, our employees have turned to the unmanned aerial vehicles as a way to help with challenging line restoration work.
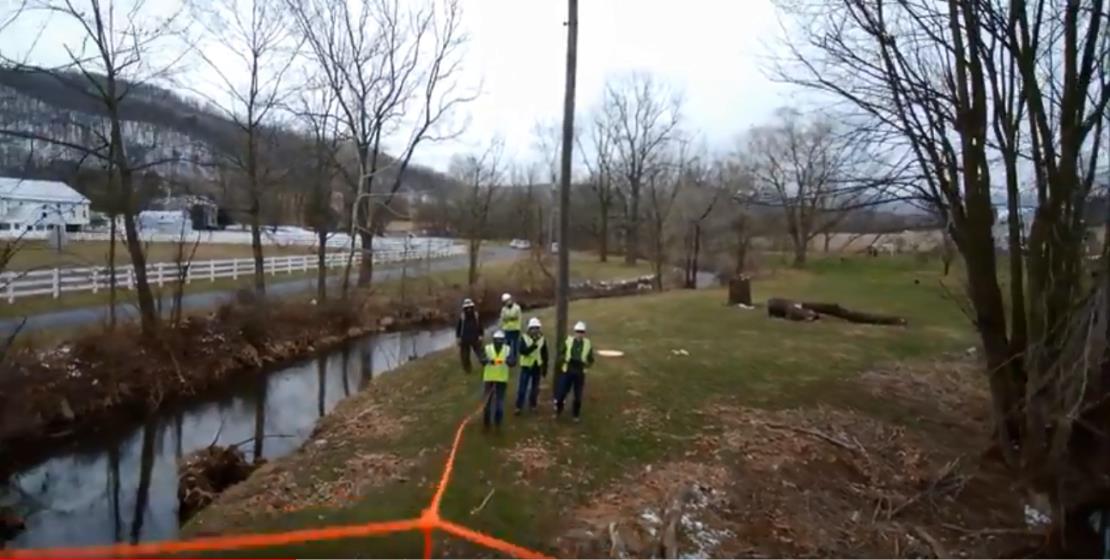
During recovery from the March 2 nor’easter, crews used a drone to help with a difficult job in the Shohola, Pike County, area. Crews had to get a line through a 1,200-foot section of ravine, with a downed tree blocking the right of way.
Regional Design Supervisor Bill Farber remembered hearing that Regional Design Supervisor Phil Brant had used a drone to help string lines during restoration work in Puerto Rico. A drone was used there on three separate occasions to fly a pulling string across inaccessible areas ranging from 150 to 500 feet across. Crews were then able to use the string flown in by the drone to pull line across the inaccessible areas.
Just as he did in Puerto Rico, Brant used a drone to fly a piece of line across the 1,200-foot ravine, proving PPL can achieve flights of greater length with continued success.
While other methods can be used to pull string through inaccessible areas, drones offer a more controlled, precise and safe way to do so.
“Using drones for this purpose can save the company money and help us get lines rebuilt more quickly,” Farber said.
A drone also proved to be the right solution to a different weather-related challenge in the Harrisburg region.
In the Newport area, a single-phase line crosses Sherman Creek, which has an island in the middle. During the week of March 12, a tree on the island fell and took down the line.
The creek was too swollen for crews to wade across. So Field Supervisor Andy Breault reached out to Senior Engineer Tom Grosz, asking whether the drone used at the Lancaster Service Center might be usable.
The method was the same: Support Engineer Eric Resch attached a rope to the drone and flew it across the creek. The crew then used the rope to pull a new line across the creek. The drone flight took just 10 minutes for setup and five minutes to fly, Resch said.
“I flew the drone past the crew, and the rope dropped off the drone and pretty well landed right in their hands,” he said.
Of course, power line inspections continue to be the primary use for drones. But the aerial vehicles also are proving their worth in other ways.


0 Comments